7- شرح زمن الماضي البسيط بالتفصيل
7- شرح زمن الماضي البسيط بالتفصيل
تعريف زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple
ما هو زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple هو الزمن الذي نستخدمه للتحدث عن فعل أو حدث وقع في الماضي وانتهى . وتاليا شرح مفصل بإذن لله عن زمن الماضي البسيط
شكل الجملة المثبتة في زمن الماضي البسيط
تتكون الجملة في زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple كما هو موضح في الجدول التالي :
| object | V.2 | I he She It They We You |
شكل الجملة في past simple
*V.2: أي التصريف الثاني للفعل .
نلاحظ من الجدول السابق أن الماضي البسيط لا يفرق بين الجمع والمفرد في الجملة المثبته positive sentence فهي تتكون من :
فاعل + التصريف الثاني من الفعل
مثال:
I played football yesterday
أنا لعبت كرة القدم بالأمس
Mary liked skating when she was a girl
أحبت ماري التزلج عندما كانت فتاة .
تحويل الفعل إلى التصريف الثاني
كما قلنا أن الفعل نحوله في past simple إلى V2 وتنقسم هنا الأفعال إلى قسمين أفعال منتظمة ( regular verbs) و أفعال غير منتظمة ( irregular verbs ).
الأفعال المنتظمة
نضيف (ed) للفعل المنتظم وهذا يسري على جميع الأفعال المنتظمة في اللغة الإنجليزية الا التي تنتهي بحرف (y) بحيث نحذف حرف (y) في آخر الكلمة ونضيف (ied) وتاليا جدول توضيحي
| التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى بالماضي |
| watched | watch | شاهد |
| studied | study | درس |
| carried | carry | حمل / نقل |
| liked* | like* | أحب |
*عندما تنتهي الكلمة ب (e) مثل (like) نضيف فقط (d) كما هو موضح في الجدول
الأفعال الشاذة في Past Simple Tense
لا تنطبق على الأفعال الشاذة قاعدة (ed) لتحويلها للتصريف الثاني في جملة زمن الماضي البسيط
فلا بد من حفظ تصاريف الأفعال الشاذة ولكن لا تخف
نحن في موقنا أفردنا لها موضوع خاص وقمنا بكتابتها وتوزيعها على 17 عشرة مجموعة لكي يسهل عليك حفظها بأسرع وقت بإذن الله .
| التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى بالماضي |
| blew | blow | هجم |
| broke | break | كسر |
| learnt | learn | تعلم |
| spent | spend | أنفق |
| slept | sleep | نام |
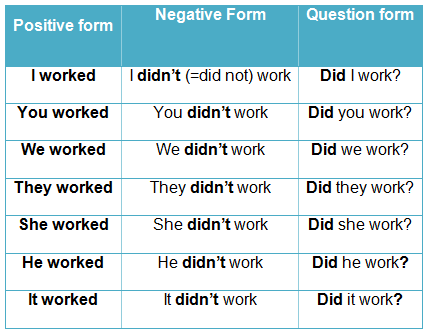
النفي في زمن الماضي البسيط
في حالة النفي (negative sentence) نستخدم (did+not) وتختصر ب ( didn’t ) مع ارجاع الفعل إلى التصريف الأول
مثال:
. He didn’t watch the movie last week
هو لم يشاهد الفيلم الأسبوع الماضي .
. I didn’t go to Aqaba when I was child
لم أذهب الى مدينة العقبة عندما كنت صغيرا.
وهذا يعني اني لم اذهب وانا صغير ولا يعني اني لم اذهب الى العقبة عندما كبرت .
تركيب الجملة بالنفي:
| adverb | object | V.1 | didn’t | I he She It They We You | |
| yesterday | their homework | do | didn’t | They |
السؤال في زمن الماضي البسيط Past Simple
| ?V.1 | I he She It They We You | Did |
| ?play | you | Did |
بعد دراسة الجدول السابق نلاحظ أن Did تأتي في بداية السؤال ثم الفاعل ثم الفعل في حالته الأولى أي التصريف الأول من الفعل.
أمثلة
?Did you read book last month
.Yes, I did
أو
.No, I didn’t
صيغة سؤال (Wh) في Past Simple Tense
سؤال ( wh) نضع أداة (wh) في بداية السؤال ثم did ثم الفاعل تاليا التوضيح.
| ?go | I he She It They We You | did | Wh-question |
| ?go | you | did | Where |
مثال :
?Where did you go last weekend
I went to the Dead Sea last weekend
الكلمات الدلالية على زمن الماضي البسيط
لا يشترط وجود كلمات دلالية (Kyewords) في الجملة لكي نعلم انها ماضي بسيط فمن المعنى السياقي نعلم انهى ماضي بسيط خاصة ان كانت فقرة او أكثر وتاليا بعض الكلمات التي تدل على زمن الماضي البسيط.
Yesterday
Last week
Last month
Last year
Last night
Ago
ذات مرة Once
في يوم من الأيام Once upon a time
في السنوات الماضية وكل تاريخ دل على الماضي In 2017 / 1988
في الأيام الماضية أو الخوالي In olden days
عندما كنت طفلا أو صغيرا When I was child
في طفولتي In my childhood
في أيام طفولتي In my boyhood days
صباح اليوم Today morning
تمارين على زمن الماضي البسيط
1- I __________ (like) when I was 7 years old
2- Today morning, I__________ (brush) my teeth
3- ?What time ______________ (she/get up) yesterday
4- They ________________ (wake up) very late yesterday
5- Ali _________________ (not/use) the computer last week
6- She __________(make) good meal
7- He ___________ (live) in Saudi Arabia last year
8.They_______________ (not/study) for the exam last nigh
9-? Why___________ (it/come)
10- I ___________________ (not/watch) football match
شرح زمن الماضي البسيط (Past Simple Tense) في اللغة الإنجليزية
إن الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية من الأزمنة التي من السهل تطبيقها على الجمل إذا تم فهمها بالشكل الصحيح، لهذا سوف نساعدكم على فهم هذا الزمن بسهولة مع توفير الأمثلة التي تساعد على الشرح.

الماضي البسيط في اللغة الانجليزية
قبل البدء في شرح كيفية استخدام الماضي البسيط وتكوينه يكون علينا معرفة ما هو الماضي البسيط، في بعض الأحيان نُطلق على الماضي البسيط صيغة الماضي.
حيث يتم استخدامه من أجل التعبير عن فعل قد اكتمل في فترة زمنية حدثت من مدة تسبق الوقت الحالي، وهو الصيغة الرئيسية التي تقوم بالتعبير عن الماضي في اللغة الإنجليزية.
لهذا عند استخدام زمن الماضي البسيط يكون ذلك إشارة إلى حدث قد تم في الماضي القريب أو الماضي البعيد، وقد لا نحتاج إلى توضيح وقت حدوث الفعل.
تكوين زمن الماضي البسيط
ينقسم تكوين الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية إلى عدة أقسام وهي:
الإيجاب(positive)
إن استخدام الماضي البسيط في حالة الإيجاب تكون من خلال استخدام التصريف الثاني من الفعل والذي يكون عبارة عن الفعل يُضاف له ed، أي يكون مثلtalk يكون تصريفها الثاني talked
ويكون تكوين الجملة في الماضي البسيط
Subject + Verb(-d, -ed, -ied)
أمثلة:
I played handball last week
لعبت كرة اليد الأسبوع الماضي
He visited France last month
زار فرنسا الشهر الماضي
I studied hard last week
لقد درست بجد الأسبوع الماضي
وتنقسم الأفعال إلى عدة أنواع
أفعال عادية
وهي تكون عن أفعال يتم إضافة ed في نهايتها، مثل
play → played
هناك أفعال تنتهي بحرف y يتم تغيرها إلى i ثم تُضاف ed، وهي الأفعال التي لا تنتهي بأحد هذه الحروف (a, e, u, o, i) وتنتهي بالحروف الساكنة مثل
carry → carried
على أن تكون أمثلتها هي: هو لعب كرة قدم أمس He played football yesterday.هي حملت حقيبتها She carried her bag
أفعال شاذة
وهي تكون عبارة عن أفعال في تصريفها الثاني لا يتم إضافة ed لها بل يكون لكل فعل شكل مختلف في تصريفه، وهي مثل
| الشكل الرئيسي | الماضي البسيط |
| Be | was/were |
| Give | gave |
| Have | had |
| Go | Went |
| Do | did |
| Eat | ate |
| Write | wrote |
وتكون أمثلتها:
I went to Algeria last week
ذهبت إلى الجزائر الأسبوع الماضي
She gave me some food
أعطتني بعض الطعام
I wrote a book
لقد كتبت كتابا
النفي (Negative)
يكون تكوين الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية في حالة النفي عبارة عن استخدام الفعل في حالته الأصلية ولكن يسبقه did not أي يكون تكوين الجملة هو
Subject + Did + Not + Base verb
وتكون الأمثلة عليها
I did not (didn’t) play football last week لم ألعب كرة القدم الأسبوع الماضي
They did not (didn’t) work last month لم يعملوا الشهر الماضي
he did not (didn’t) go to the party last weekend لم يذهب إلى الحفلة نهاية الأسبوع الماضي
السؤال (Yes / No Questions)
في حالة السؤال (Yes / No Questions) في صيغة الماضي البسيط ويكون الرد عبارة عن Yes or No تكون صيغة السؤال هي
?Did + Subject + Base verb
ومن أمثلتها
?Did you go to the park yesterday هل ذهبتم إلى الحديقة الأمس
? Did she leave last night هل غادرت الليلة الفارطة
? Did you read the novel ? هل قرأت الرواية
وتكون الإجابة عبارة عن Yes أو No
السؤال (Wh Questions)
وهي عبارة عن أسئلة يكون بها أحرف W أو H مثل When للزمان أو Where للمكان
صيغة السؤال تكون على النحو التالي
?WH + Did + Subject + Base verb
مثل:
?Where did you go last week
إلى أين ذهبت الأسبوع الماضي؟
?What did you eat for dinner yesterday
ماذا أكلت في العشاء البارحة؟
?When did he wake up this morning
متى استيقظ هذا الصباح؟
الإجابة على هذا النوع من الأسئلة تكون عن طريق تقديم المعلومة المطلوبة من عند السائل بالضبط (مثل السبب، الزمان، المكان…)
الحالة الخاصة للفعل to be في الماضي
إن الفعل to be في الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية يكون له تصريف مختلف، وتتكون جملته من
Subject + Be(Was/were)
ويكون تصريفها:
- I، He، She، It تكون Was
- You، We، They تكون Were
من أمثلتها في حالة الإيجاب:
I was sick yesterday كنت مريضا البارحة
We were in London last week لقد كُنا في لندن الأسبوع الماضي
It was cold yesterday . كان الجو بارداً البارحة
النفي
تكون صيغته
Subject + (Was/were) + Not
أي أنه مع كل تصريف يتم إضافة Not للفعل، مثل:
I was not (wasn’t) busy yesterday. لم أكن مشغولا الليلة البارحة.
They were not (weren’t) in Egypt . لم يكونوا في مصر.
It was not (wasn’t) cloudy yesterday . لم يكن الجو غائم في البارحة
السؤال (Yes / No Questions)
ويكون تكوينه عبارة عن
?……Be(Was/were) + Subject
مثل:
?Were you sick yesterday هل كنت مريضًا البارحة
?Was it hot yesterday هل كان الجو حاراً البارحة
Was he a doctor last year? هل كان طيباً العام الماضي الجواب على هذا النوع من الأسئلة دائما يكون نعم أو لا، لذلك سميت ب Yes / No Questions
السؤال (Wh Questions)
يكون تكوين السؤال
?……WH + Be(Was/were) + Subject
مثل:
?Where were you last month
أين كنت الشهر السابق؟
?How was your night
كيف كانت ليلتك؟
?Why was she angry this morning
لماذا كانت غاضبة هذا الصباح ؟
الإجابة على هذا النوع من الأسئلة يكون عن طريق تقديم المعلومة المطلوبة من عند السائل (مثل المكان، الزمان، السبب…)
استخدامات زمن الماضي البسيط
1_إن زمن الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية يُعبر عن أحداث قد وقعت وانتهت في وقت مضى، والتي تعبر عنها هذه الصورة:
مثل:
I went to the garden last week and
ذهبت إلى الحديقة نهاية الأسبوع الماضي .
John played football yesterday
لعب جون كرة القدم البارحة .
Yahya traveled to Italy last month
سافر يحيى إلى إيطاليا الشهر الماضي.
2_وأيضًا يُعبر عن مجموعة أحداث انتهت أيضًا في فترة مضت، وتكون على النحو التالي:
مثل:
I finished work, walked to the garden, and found a nice place to run
انتهيت من العمل، ذهبت إلى الحديقة، و وجدت مكان جميل للجري.
First I got up, then I brushed my teeth
أولاً استيقظت ، ثم غسلت أسناني.
الكلمات الدالة على الماضي البسيط
هناك بعض الكلمات التي تدل على الماضي البسيط في اللغة الإنجليزية مثل:
| مثال | الكلمة الدالة |
| It was cloudy last night | Last…. |
| She was a doctor 9 years ago | Ago |
| I worked in Chicago in 2018 | In… |
| I didn’t sleep well yesterday | Yesterday |
شرح الماضي البسيط بالتفصيل شرح قاعدة past simple
شرح الماضي البسيط بالتفصيل التعريف
الماضي البسيط : هو كل حدث (فعل) بدا وانتها في الماضي وعندما نتحدث عنه نذكره على أنه تم سواء كان فعل قمنا به أو حدث تم أو نشاط فعلناه أو قام به غيرنا.
عندما نتحدث عن الماضي البسيط لابد أن نلزمه ونحدد وقت الحدث بذكرنا لكلمات تدل عليه مثل: yesterday, last, ago عندما نجد أحد تلك الكلمات أو كلمات مماثلة في الجملة نعلم مباشرة أنها في الماضي البسيط. في حال انه لم يتم ذكر الوقت في الجملة فأنه يكون مضارع تام.
شرح قاعدة past simple طريقة تكوين الجمل
من السهل جدا أن نكون جملة في الماضي البسيط فأي جملة تتكون من فاعل قام بالفعل وفعل تم ومفعول به وقع عليه الفعل إذا تكون كالآتي:
subject+ verb+(ed)+ object
كأن نقول مثلا: I studied my lessons “أنا ذاكرت دروسي” الفاعل كان I، الفعل كان studied، المفعول به الذي وقع عليه فعل المذاكرة كان
my lessons
ملاحظة هامه جداً، حينما استخدمنا الفعل يذاكر استخدمناه في الماضي بمعنى “ذاكرت” والذي ميز الفعل أنه بالماضي هو إضافة “ed” إذا القاعدة العامة تقول: أي فعل ماضي ينتهي ب “ed” ماعدا بعض الأفعال يطلق عليها الأفعال الشاذة مثل write “يكتب” في الماضي تكتب wrote فإذا وجدناها كذلك علمنا أنها بالماضي البسيط. .
a) Sarah walked to the downtown yesterday
ذهبت (مشت) سارة الى وسط المدينة أمس
b) I slept for 8 hours last night
انا نمت لمدة 8 ساعات ليلة امس
slept=sleep وهي فعل شاذ
هنا نجد في المثالين a,b أن الماضي البسيط استخدمناه للحديث عن الأنشطة أو المواقف التي بدأت وانتهت في الماضي سارة ذهبت امس اي الفعل تم بالماضي وانتهى ولم يمتد لوقت الكلام. وكذلك أنا نمت الليلة السابقة فهو قد نام واستيقظ وأخبر أنه فعل ذلك ليلة البارحة.
وما ميز الجملة الفعل walked المضاف له ed والفعل slept الذي أساسه sleep وتتم كتابته هكذا دون إضافة ed لأنه فعل شاذ كما ذكرنا سابقا، ما ميز الجملة أيضا أنها في الماضي الكلمات (yesterday, last night)
شرح قاعدة past simple امثلة على past simple
c) Ahmad stayed at home yesterday
ظل احمد في المنزل أمس
d) Our flight arrived on time last night
طائرتنا وصلت في الميعاد ليلة أمس
في المثالين c,d نجدأن معظم الأفعال في الماضي البسيط تنتهي ب ed.
e) I ate breakfast this morning
أنا أكلت فطوري هذا الصباح
f) Samir took a taxi to the airport yesterday
سمير أخذ تاكسي إلى المطار أمس
في المثالين نجد أن بعض الأفعال تكون شاذة في تكوين الماضي فالفعل ate أساسه eat، والفعل took أساسه take
نلاحظ انه تم ذكر a قبل كلمة taxi اي ان التاكسي مجهول غير معلوم للمستمع،
g) I was busy yesterday
أنا كنت مشغول أمس
h) they were at home last night
هم كانوا بالمنزل ليلة أمس
في المثالين نجد أن الماضي البسيط الذي يتكون من الفعل يكون be يتحول إلى الصيغة was لو كان مع المفرد و were لو كان مع الجمع.
المقصود بـ الفعل be هو is-are هذه في حالة المضارع اما في حالة الماضي تتحول الى was-were
is=was
are=were
الصورة القادمة توضح السؤال في الماضي البسيط و نفي الماضي البسيط
امثلة صحيحة على استخدام شرح الماضي البسيط بالتفصيل :
1) I found this wallet under the chair 2 hours ago
أنا وجدت هذه المحفظة تحت الكرسي قبل ساعتين
هنا جملة الماضي البسيط تميزت بالفعل found الذي أساسه find وكتبت هكذا بالماضي البسيط لأنها فعل شاذ.
2) he completed his task in the last hour
هو أكمل مهمته في الوقت المحدد الساعة الماضية
تميز الفعل في الماضي البسيط هنا بإضافة ed وأساس الفعل complete فأضفنا d فقط لأنه أساسا منتهي ب e وليس صحيحا أن نضيف e زائدة completed هكذا خطأ.
الصورة القادمة توضح متى وكيف نضيف ed-d-ied الى نهاية الكلمات في الماضي البسيط وبقية الازمنة
3) Noor asked her sister to help her 2 hours ago
نور سئلت\طلبت من أختها أن تساعدها منذ ساعتين
الذي ميز جملة الماضي البسيط هنا الفعل asked و ago منذ ساعتين من الكلمات الدالة على الماضي.
امثلة خاطئة على شرح قاعدة past simple
He write his homework last night (1
هو يكتب واجبه ليلة أمس
الخطأ ب write لأنها في زمن المضارع والكلام بصيغة الماضي البسيط الصواب: wrote
2) Heba eated her sandwiches at the break
الخطاء هو كتابة eated بسبب انها من الأفعال الشاذة، والصحيح كتابتها ate
3) did she walked to the school yesterday
الخطأ هنا أنه إذا سألنا في الماضي البسيط يتحول الفعل في الماضي إلى أصله فكان يجب أن يستبدل الفعل walked الى walk ذالك ان did هي الماضي من does ونكتفي بفعل واحد في زمن الماضي وهذه قاعدة هامة
4) she is happy when she was at school
هي كانت سعيدة عندما كانت في المدرسة
الخطأ في is والصواب was لأن ذلك كان وصف بالماضي لتصبح الجملة
she was happy when she was at school
5) they visit their parents last Friday
هم زارو والديهم في يوم الجمة الماضية
الخطأ في visit والصواب visited لأن الجملة بالماضي.
تمارين زمن الماضي البسيط Past simple مع الحلول

التمرين الأول لزمن الماضي البسيط Past simple
صرف الأفعال الآتية مما بين القوسين:
1- I (not drink) any beer last night
2- I (help) my mother in the kitchen
3- She ( get on) the bus in the center of the city
4- I (not change) trains at Victoria
5- They (wash) their clothes in the bathroom
6- We (watch) an interesting film yesterday
7- We (wake up) very late
8- We (not use) the computer last night
9- They (live) in London
10- Students (work) in the garden
11- A lot of people (skate) on the lake
12- The teacher (plant) a tree
13- Sarah (want) a new dress
14- He (not study) for the exam
15- She (read) the newspaper yesterday
16- ?( she/ make) good coffee
17- I (look) through the window
18- We (search) for information
19- They (work) in the morning
20- Ahmed (clean) the house
حل التمرين الأول لزمن الماضي البسيط Present simple
1- I didn’t drink any beer last night
2- I helped my mother in the kitchen
3- She got on the bus in the center of the city
4- I didn’t change trains at Victoria
5- They washed their clothes in the bathroom
6- We watched an interesting film yesterday
7- We woke up very late
8- We didn’t use the computer last night
9- They lived in London
10- Students worked in the garden
11- A lot of people skated on the lake
12- The teacher planted a tree
13- Sarah wanted a new dress
14- He didn’t study for the exam
15- She read the newspaper yesterday
16- ?Did she make good coffee
17- I looked through the window
18- We searched for information
19- They worked in the morning
20- Ahmed cleaned the house
التمرين الثاني لزمن الماضي البسيط Past simple
اختر الإجابة الصحيحة مما بين القوسين:
1- He ( works – worked – work ) in a bank
2- You ( don’t call – didn’t call – doesn’t call ) me yesterday
3- I ( visit – visiting – visited ) lots of interesting places
4- In the morning we ( walked – did walk – have walked ) in the streets of London
5- It ( don’t rain – didn’t rain – haven’t rain ) a lot yesterday
6- She ( didn’t like – not liked – won’t liked ) Chocolate
7- I ( don’t forget – didn’t forgot – didn’t forget ) your book
8- Sarah ( met – meet – mate ) a friend
9- Last year I ( go – went – did go ) to London on holiday
10- The movie ( was – were – did ) fantastic
11- We ( see – saw – seen ) some beautiful rainbows yesterday
12- The weather ( were – was – did ) strangely fine
13- We ( move – moved – did move ) to a new house last week
14- Sarah ( miss – missed – misses ) the bus
15- They ( buy – bought – buys ) a sandwich
16- Ahmed didn’t ( watch – watches – watched ) television
17- They ( sell – sold – selling ) their car last year
18- She ( read – reading – reads ) a book last night
19- The student ( was – did – were ) very cleaver
20- The teacher ( was – did – were ) nice
حل التمرين الثاني لزمن الماضي البسيط Past simple
1- He worked in a bank
2- You didn’t call me yesterday
3- I visited lots of interesting places
4- In the morning we walked in the streets of London
5- It didn’t rain a lot yesterday
6- She didn’t like Chocolate
7- I didn’t forget your book
8- Sarah met a friend
The simple past tense of the verb to be
This page will present the simple past tense of the verb to be
- its form
- and its use
The affirmative form
| I, he, she, it | was |
|---|---|
| you, we, they | were |
Examples
- I was in London in 1999
- Pam was in London in 1999, too
- We were together
- She was my girlfriend
The interrogative form
| Was | ?I, he, she, it |
|---|---|
| Were | ?you, we, they |
Examples
- ?Were you in London last year
- ?Was Pam with you
- ?Were you together
The negative form
| I, he, she, it | was not |
|---|---|
| wasn’t | |
| You, we, they | were not |
| weren’t |
Examples
- I wasn’t in Paris in 1999
- Pam wasn’t in Paris in 1999
- We weren’t in Paris
Use of the simple past
The simple past is used principally to describe events in the past
Remember
1. wasn’t is the short form of was not. You can say either
- I was not in Paris, or
- I wasn’t in Paris
2. weren’t is the short form of were not. You can say either
- we were not in Paris, or
- we weren’t in Paris
Past Simple Tense
you cam watch tis video for more info
The Past Simple Tense is used to refer to actions that were completed in a time period before the present time. In the Simple Past the process of performing the action is not important. What matters is that the action was completed in the past. The action may have been in the recent past or a long time ago
So let’s start learning the Simple Past Tense – one of the most common tenses in spoken English – and the points to pay attention to
Using the Simple Past Tense
The Simple Past is used for actions that started and finished at a specific time in the past. It’s also possible to use the simple past in a sentence without specifying a time, but it must have previously been made clear that the speaker is referring to a finished period
I saw a movie last week
The Simple Past is used to describe several actions that were completed in the past
I finished work, walked to the beach and met my friends
The Simple Past is used to describe a process that started and finished in the past. In this case, the process of the action is long and is used by specifying time periods such as ‘the whole year’ or ‘all day’
I lived in Italy for five years
The Simple Past can also be used in sentences that describe past habits. These sentences have the same purpose as the expression ‘used to’. It should be clear in this kind of sentence that the action referred to is a habit. Time expressions like always, often, usually and never can be used to underline this
I often played football when I was a young man
Forming the Simple Past
Affirmative sentences in the Simple Past
In affirmative sentences the word order is subject + verb and the form of the verb in the simple past is the same for all subjects (with the exception of ‘to be’ – was/were)
Subject + past simple + object
For example
I played football yesterday
He saw his family last week
I was in France in June
Negative sentences in the Simple Past
To make negative negative sentences in the simple past we use the auxiliary ‘did not’ / ‘didn’t’ and the base form of the verb
Subject + did not + base form of verb + object
For example
I didn’t play football yesterday
They didn’t go to the theater last month
She didn’t arrive on time this morning
Questions in the Simple Past
To make questions in the simple past we use ‘did’ in front of the subject and base form of the verb.
?Did + subject + base form of verb + object
For example
?Did you play football yesterday
?Did they lose the match
?Did he clean his home last weekend
Regular and Irregular Verbs
In order to convert regular verbs from their base form to the simple past form, we add -ed. For irregular verbs, however, the simple past form doesn’t follow this rule and can vary significantly and you simply need to learn them by heart. There are many irregular verbs but below you can find the most common ones that you need to know for daily use
Regular verb examples
place – placed
dance – danced
plan – planned
stop – stopped
fix – fixed
snow – snowed
rain – rained
need – needed
help – helped
add – added
worry – worried
play – played
As you can see from these examples, with most regular verbs we add -ed. When a verb ends in -e we simply add -d. And when a verb ends in a consonant and -y, we change the -y to -i and add -ed
Irregular verb examples
be – was/were
buy – bought
come – came
do – did
eat – ate
find – found
go – went
have – had
leave – left
make – made
pay – paid
see – saw
take – took
tell – told
write – wrote
By learning the simple past you can describe many things about your personal and professional life. So start practicing it now by doing this fun quiz
How to Learn Regular and Irregular English Verbs
In order to use many verb tenses in English, you need to know the past forms of the verbs. All verbs have a base form or ‘infinitive’ (for example, look, make, play). The majority of verbs, called ‘Regular verbs’, follow the same pattern and create the past simple and the past participle using the same word ending -ed. There are, however, verbs that have different endings
and these are called ‘Irregular verbs.’ At Wall Street English you learn the regular and irregular verbs gradually throughout your course, which makes them easier to learn and remember. Here is a “how to learn regular and irregular verbs” with examples and also some tips on how to remember them
An Overview of English Verb Forms
Every verb in English can have a base form, an -ing form, a past simple form and a past participle
We use the base form for
the present simple tense. For example “They live in Rome
the infinitive. For example, “I want to learn English
We use the -ing form (or the gerund) for
continuous tenses, like the present continuous. For example. “He’s working
verbs as nouns. For example, “Swimming is good for you
And we use the past participle for
perfect tenses, like the present perfect. For example, “I’ve finished
the passive form. For example, ”It was made in Japan
adjectives. For example. “The chair is broken
?What are Regular Verbs
Regular verbs in English create the past simple and past participle by adding -ed to the base form
For example

If the verb ends in a consonant and -y, we change the -y to -i and added -ed. For example
If a verb ends in -e we simply add -d, For example
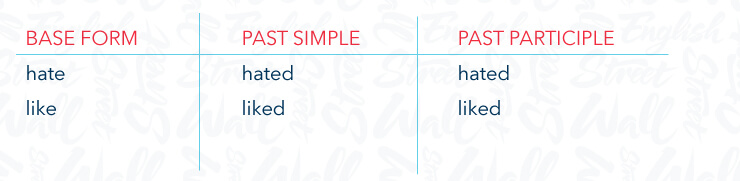
Here are some examples of regular verbs
“Yesterday Jack studied all day
“Raul has accepted the job offer
?“Have you finished yet
“We really liked the film we watched last night
There are three ways to pronounce -ed, depending on the last letter of the verb
?What are Irregular Verbs
There are about 200 irregular verbs in English. We can divide these into four types
Verbs which have the same base form, past simple and past participle
Verbs which have the same past simple and past participle
Verbs which have the same base form and past participle
Verbs which have a different base form, past simple and past participle
A good way to learn irregular verbs is to study them in these groups because as they are similar they’re easier to remember. Here are the most common irregular verbs in these groups
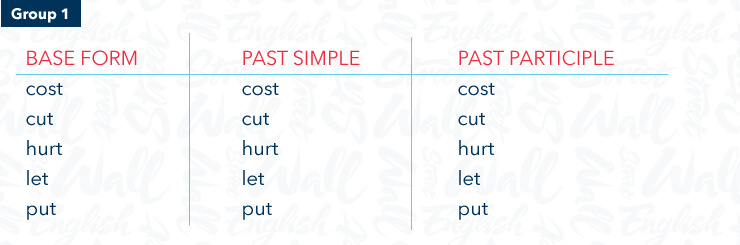
For example
“Our car cost a lot of money but it’s always breaking down
“Pasha hurt himself in a soccer match last weekend
“My parents have let me stay out late tonight
“They put on their jackets because it was very cold
For example
“They had lunch at a Thai restaurant on Monday
?“Have you heard the news about the train strike
“Tim has sent an email to all the suppliers
“Who won the match?” – “The Giants

For example
“He came back home at 4 a.m. on Saturday
“Suzi has become the Managing Director
“The dog ran into the garden after Lee opened the door
?“Has Mrs. O’Connor come back from lunch yet
For example
“The kids ate a lot of cakes at the party
“They drove to the airport and left their car there
?“Has she taken her tickets yet
“I’ve written a letter of application for the manager’s job
Learning tips
So, what’s the best way to learn all these irregular verbs
Pay attention when you see a new verb in your interactive lesson and then in your digital workbook
Make your own examples for every new verb you find
Do the exercises about irregular verbs online or test your English level with this English Test
Keep a diary in English and write down a few things you did every day
Read a Learner’s book in English. Books are full of verbs in their past forms, so reading is a really useful way to practice and review. Your Wall Street English Center probably has some books available for you to borrow
Focus on learning a few irregular verbs at one time
Join complementary classes and social club activities at Wall Street English to get extra practice in using regular and irregular verbs
الأفعال الشاذة في اللغة الإنجليزية مترجمة في 17جدول ملون وملف pdf
عقدة حفظ الأفعال الشاذة في اللغة الإنجليزية
الأفعال الشاذة في اللغة الإنجليزية ليست البعبع الكبير الذي كان احد اهم نقاط ضعفنا باللغة الإنجليزية وربما جعلتنا الأفعال الشاذة نزداد رهبة من اللغة الإنجليزية ولكن هل انت مستعد لتغيير هذه الفكرة .
سوف تغيرون وجهة نظركم بإذن الله بعد اطلاعكم على جدول الأفعال الشاذة الذي اعددناه لكم
والمقسم لعدة مجموعات لكي يسهل حفظها عليكم بإذنه تعالى.
تنقسم جميع الأفعال في اللغة الإنجليزية من حيث التصريف الى قسمين
وهي الأفعال المنتظمة (regular verbs)
و الأفعال الشاذة ( irregular verbs ) :
الأفعال المنتظمة (regular verbs)
وهي الأفعال التي نضيف لها (ed ,ied) في التصريف الثاني والثالث للفعل وتاليا أمثلة على ذلك:
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| played | played | play | يلعب |
| studied | studied | study | يدرس |
| liked | liked | like | يحب |
| improved | improved | improve | يتحسن |
| carried | carried | carry | يحمل |
الافعال الشاذة irregular verbs
الأفعال الشاذة أو الغير منتظمة هي الأفعال التي لا تنطبق عليها قاعدة (ed) عند تصريفها
ولذلك لابد من حفظها وهي مزعجة لمن يريد تعلم اللغة الإنجليزية
فلا مفر من حفظها ان اردت ان تتعلم اللغة الإنجليزية .
ايهما اكثر الأفعال الشاذة ام المنتظمة
بكل تأكيد الأفعال المنظمة أكثر بكثير ولكن الأفعال الشاذة مهمة جدا
ولا غنى عنها في اللغة الإنجليزية وهي مهمه جدا في حياتنا
وبالممارسة سوف يسهل عليك التعامل معها خاصة اذا
درستهم عن طريق الجداول التي وضعناها.
ماهي طريقة احفظ الأفعال الشاذة ؟
- ادرس الجداول 17 المذكورة في المقال
- حاول ان تحفظ 3 افعال كل يوم ويفضل في الصباح الباكر او عند النوم
- حاول أن تضع تصاريف الأفعال في جمل باستخدام الزمن الصحيح
لماذا جدول الأفعال الشاذة على موقع التحدي ؟
نحن في موقعنا قمنا بتقسيم هذه الأفعال على سبعة عشر قسما ليسهل عليك حفظها.
واعتمدنا على أسلوب مختلف في ترتيبها فلم نرتبها هجائيا
ولكن قمنا باتباع عدة اسس لترتيبها مثل التشابه في المقطع الأخير الفعل.
وبإذن الله سوف تجد الفرق وسوف تزداد تمكين في حفظ الأفعال الشاذة
الجدول الأول من الأفعال الشاذة .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الاول | المعنى |
| blown | blew | blow | يهجم |
| grown | grew | grow | ينمو |
| known | knew | know | يعلم |
| thrown | threw | throw | يرمي |
| drown | drew | draw | يرسم |
| flown | flew | fly | يطير |
الجدول الثاني.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الاول | المعني |
| broken | broke | break | يكسر |
| spoken | spoke | speak | يتحدث |
| stolen | stole | steal | يسرق |
| chosen | chose | choose | يختار |
| frozen | froze | freeze | يتجمد |
| woken | woke | wake | يستيقظ |
الجدول الثالث.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الاول | المعنى |
| learnt | learnt | learn | يتعلم |
| meant | meant | mean | يعني |
| burnt | burn | يحرق | |
| dreamt | dreamt | dream | يحلم |
| spelt | spelt | spell | يتهجى |
| smelt | smelt | smell | يشم |
الجدول الرابع .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| spent | spent | spend | ينفق |
| sent | sent | send | يرسل |
| built | built | build | يبني |
| lent | lent | lend | يعير/يقرض |
| bent | bent | bend | ينحني |
الجدول الخامس.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| brought | brought | bring | يحضر/ يجبر |
| bought | bought | buy | يشتري |
| fought | fought | fight | يحارب |
| thought | thought | think | يفكر/ يعتقد |
| caught | caught | catch | يقبض / يمسك |
| tought | tought | teach | يدرس |
الجدول السادس.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| kept | kept | keep | يحفظ |
| slept | slept | sleep | ينام |
| swept | swept | sweep | يكنس / يمسح |
| left | left | leave | يترك / يغادر |
| felt | felt | feel | يشعر |
الجدول السابع.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| let | let | let | يسامح |
| put | put | put | يضع |
| read | read | read | يقرأ |
| shut | shut | shut | يغلق |
| cut | cut | cut | يقطع / يقص |
| hit | hit | hit | يضرب |
| hurt | hurt | hurt | يجرح |
الجدول الثامن.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| driven | drove | drive | يقود |
| ridden | rode | ride | يركب |
| risen | rose | rise | يرفع |
| written | wrote | write | يكتب |
الجدول التاسع.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| had | had | have | يملك |
| lost | lost | lose | يفقد / يخسر |
| won | won | win | يفوز |
| dug | dug | dig | يحفر |
| sat | sat | sit | يجلس |
| shone | shone | shine | يلمع |
| held | held | hold | يمسك / يحمل |
| made | made | make | يعد / يصنع |
| found | found | find | يجِد |
| heard | heard | hear | يسمع |
الجدول العاشر.
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| sworn | swore | swear | يُقسم |
| worn | wore | wear | يرتدي / يلبس |
| torn | tore | tear | يحطم / يمزق |
الجدول الحادي عشر من الافعال الشاذة
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| been | was/were | be | يكون |
| done | did | do | يفعل |
| eaten | ate | eat | يأكل |
| seen | saw | see | يرى |
| gone | went | go | يذهب |
| run | ran | run | يركض |
| gaven | gave | give | يعطي |
| fallen | fell | fall | يسقط / يقع |
الجدول الثاني عشر .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| drunk | drank | drink | يشرب |
| begun | began | begin | يبدأ |
| rung | rang | ring | يقرع / يرن |
| sunk | sank | sink | يغرق |
| sung | sang | sing | يغني / ينشد |
| swum | swam | swim | يسبح |
الجدول الثالث عشر من الافعال الشاذة .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| sold | sold | sell | يبيع |
| told | told | tell | يخبر |
الجدول الرابع عشر .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| got | got | get | يجلب / يكسب |
| forgotten | forgot | forget | ينسى |
| stood | stood | stand | يقف |
| understood | understood | understand | يفهم |
| come | came | come | يأتي |
| become | became | become | يصبح |
الجدول الخامس عشر .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| shaken | shook | shake | يهتز |
| taken | took | take | يأخذ |
الجدول السادس عشر .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| .paid | paid | pay | يدفع |
| .said | said | say | يقول |
| .laid | laid | lay | يضع / يستلقي / يضرب بقوة |
الجدول السابع عشر والاخير من الافعال الشاذة .
| التصريف الثالث | التصريف الثاني | التصريف الأول | المعنى |
| fed | fed | feed | يطعم |
| met | met | meet | يقابل / يجتمع |
إن أعجبك الموضوع فقم بنشره لتعم الفائدة وترك تعليق بالأسفل إن استطعت.

